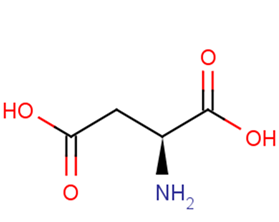
L-Aspartic acid
CAS No. 56-84-8
L-Aspartic acid( Aspartic acid | Aspatofort | EC 200-291-6 )
Catalog No. M18824 CAS No. 56-84-8
Aspartic Acid is a non-essential amino acid in humans, Aspartic Acid has an overall negative charge and plays an important role in the synthesis of other amino acids and in the citric acid and urea cycles.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 43 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Aspartic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAspartic Acid is a non-essential amino acid in humans, Aspartic Acid has an overall negative charge and plays an important role in the synthesis of other amino acids and in the citric acid and urea cycles.
-
DescriptionAspartic Acid is a non-essential amino acid in humans, Aspartic Acid has an overall negative charge and plays an important role in the synthesis of other amino acids and in the citric acid and urea cycles. Asparagine, arginine, lysine, methionine, isoleucine, and some nucleotides are synthesized from aspartic acid. Aspartic acid also serves as a neurotransmitter.(In Vitro):L-Aspartic acid is shown to be a suitable prodrug for colon-specific drug deliverly. L-[3H]Asp remaining in the brain at 5 min is increased by 206 and 178% by preadministration of 100 mM L-Aspartic acid and 100 mM L-Glu, respectively, whereas 100 mM D-Asp does not affect L-[3H]Asp efflux transport. That value for L-[3H]Glu at 20 min is increased by 145 and 156% by coadministration with 100 mM L-Aspartic acid and 100 mM L-Glu, respectively, but not by D-Asp. It is interesting that the apparent efflux rate of L-Aspartic acid across the BBB is sevenfold faster than that of L-Glu.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoL-Aspartic acid is shown to be a suitable prodrug for colon-specific drug deliverly. L-[3H]Asp remaining in the brain at 5 min is increased by 206 and 178% by preadministration of 100 mM L-Aspartic acid and 100 mM L-Glu, respectively, whereas 100 mM D-Asp does not affect L-[3H]Asp efflux transport. That value for L-[3H]Glu at 20 min is increased by 145 and 156% by coadministration with 100 mM L-Aspartic acid and 100 mM L-Glu, respectively, but not by D-Asp. It is interesting that the apparent efflux rate of L-Aspartic acid across the BBB is sevenfold faster than that of L-Glu.
-
SynonymsAspartic acid | Aspatofort | EC 200-291-6
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number56-84-8
-
Formula Weight133.1
-
Molecular FormulaC4H7NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O : 8.33 mg/mL 62.58 mM
-
SMILESC(C(C(=O)O)N)C(=O)O
-
Chemical NameL-aspartic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Leopold CS, et al. In vivo pharmacokinetic study for the assessment of poly(L-aspartic acid) as a drug carrier for colon-specific drug delivery. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1995 Aug;23(4):397-406.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tribenzylamine
Tribenzylamine is an agent of biochemical.
-
N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyeth...
N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-p-phenylenediami
-
Columbianetin beta-D...
Columbianetin-beta-D-glucopyranoside exhibits anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, it also shows strong inhibiting activity against platelet aggregation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


